Foot mycosis is the most common fungal infection on the skin today. There are three main types of foot fungus, or foot fungus, as it is otherwise called. And each type is localized to different parts of the foot and looks different.
How do you get a foot fungus?
Mycosis of the feet is caused by a fungus that grows on or in the upper layer of the skin. Mushrooms thrive best in warm, humid places. For example - in the area between the fingers. Foot fungus spreads very easily. It is enough to touch the fingers or toes of an infected person to also get sick with a high probability. But more often, fungal infection occurs when people walk barefoot on contaminated surfaces near swimming pools or in changing rooms of the same pool, gym and other similar facilities. The fungus can then stay on your shoes, especially if the shoes are too tight and air cannot circulate around your feet.
If you touch an object in which there is a fungus, after that you can also become its distributor and infect other people. Moreover, even if you infect others, it does not mean that you will definitely infect yourself. Doctors do not know why this happens, but everyone's predisposition to foot fungal infection is different. And if you have already had mycosis, there is a good chance you will get infected again.
2. Symptoms of fungus
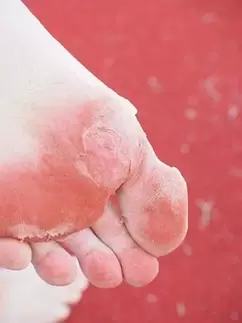
Symptoms of foot mycosis may include burning and itching of the skin between the toes. The skin may sag and crack. Other symptoms of foot fungus can vary depending on the type of athlete’s foot being diagnosed.
The first type is an infection that usually causes symptoms between the fourth and fifth toes. The skin becomes scaly, peeling and cracking. In some cases, a bacterial infection can join the mycosis and the skin condition worsens even more.
The second type of fungus is a disease that can start with slight soreness in the foot area. Then the skin on the heel or bottom of the foot thickens and may crack. As the fungus on the feet progresses, it also affects the nails. With nail fungus, it can thicken, break, or even fall off. Fungal infections of the nails and the skin of the feet should be treated differently, as a rule.
Vesicular infection is the third type of athlete’s foot. Typically, this type of foot fungus starts with fluid-filled blisters under the skin. Bubbles usually form on the bottom of the foot, but they can be found elsewhere on the foot. An accompanying bacterial infection can also develop with this type of foot fungus.
3. Diagnosis of mycosis
To diagnose a foot fungus, a doctor, as a rule, should only examine the patient and study the medical history (symptoms, previous illnesses). If the fungus on your feet is unusual or does not respond to treatment, your doctor may take a sample of your skin or nails to test for the fungus.
Not all foot skin problems are mycoses, or foot fungus. If you suspect you have a fungus but have never had it before, it actually makes sense to visit a good dermatologist.
4. Treatment of the disease
To treat a foot fungus, special lotions, lotions or sprays are usually sufficient. In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe over-the-counter pills or topical remedies to treat toenail fungus. It is necessary to treat the fungus as much as the doctor says. This will be a guarantee that it was really possible to completely cure the fungus. In addition to the general treatment of foot mycosis, it is essential that the feet be clean and dry. Mushrooms need warm, moist places to grow.
To prevent mycosis and recurrence of foot fungus, you should use your special shoes when you go to the gym, pool and similar places. To keep your feet dry, you can use talcum powder or special products. Sandals or shoes that are not too tight will ensure adequate air circulation and humidity.
























